FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC)
ASSORTED BIOPSIES
DRAINAGE
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC)
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC)
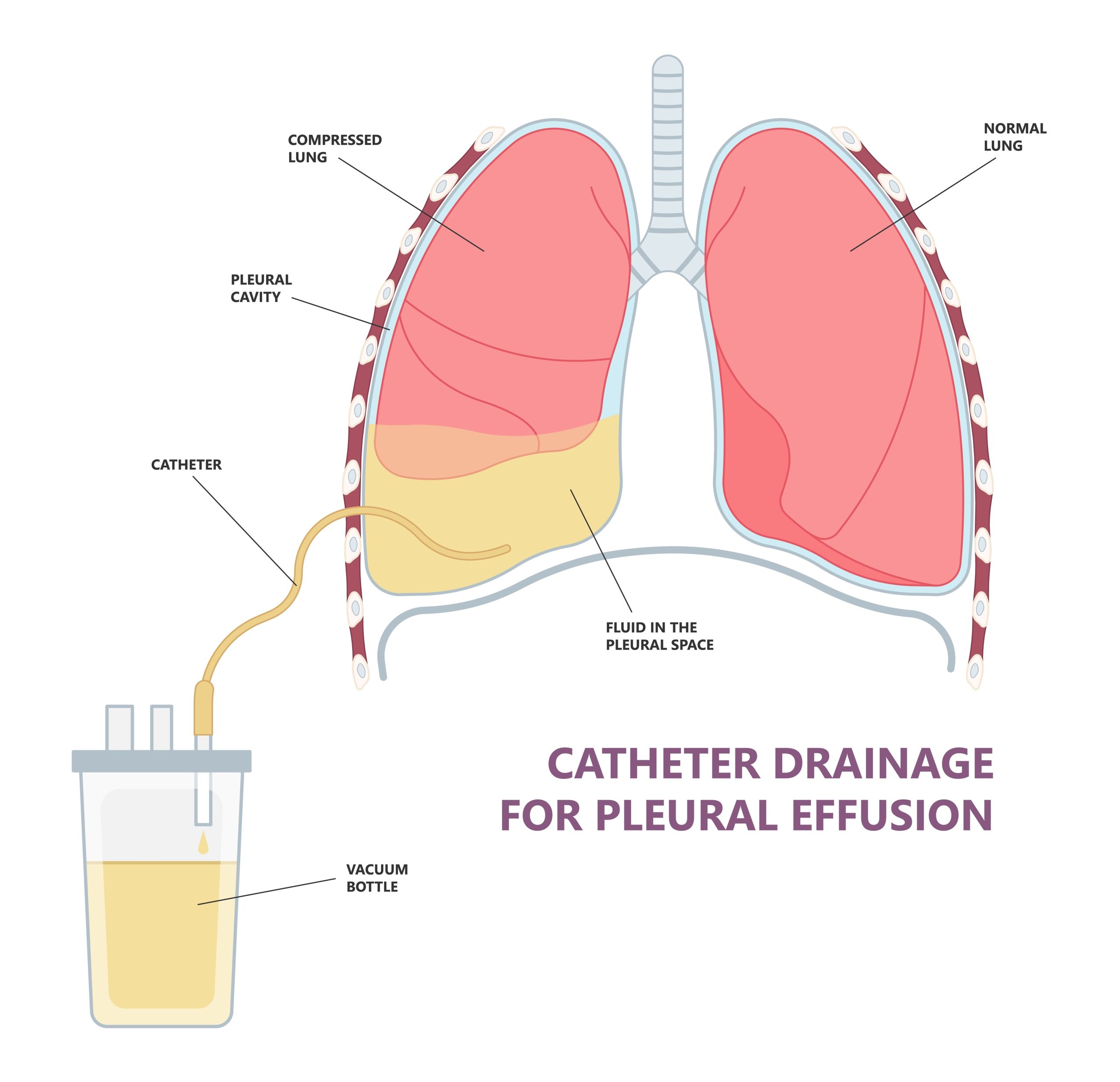
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a simple, quick and inexpensive method that is used to sample superficial masses like those found in the neck and is usually performed in the outpatient clinic. It causes minimal trauma to the patient and carries virtually no risk of complications. Masses located within the region of the head and neck, including salivary gland and thyroid gland lesions can be readily diagnosed using this technique.
ASSORTED BIOPSIES
ASSORTED BIOPSIES
- Needle Biopsy: Most biopsies are needle biopsies, meaning a needle is used to access the suspicious tissue.
- CT-Guided Biopsy: A person rests in a CT-scanner; the scanner’s images help doctors determine the exact position of the needle in the targeted tissue.
- Ultrasound-guided Biopsy: An ultrasound scanner helps a doctor direct the needle into the lesion.
- Bone Biopsy: A bone biopsy is used to look for cancer of the bones. This may be performed via the CT scan technique or by an orthopedic surgeon.
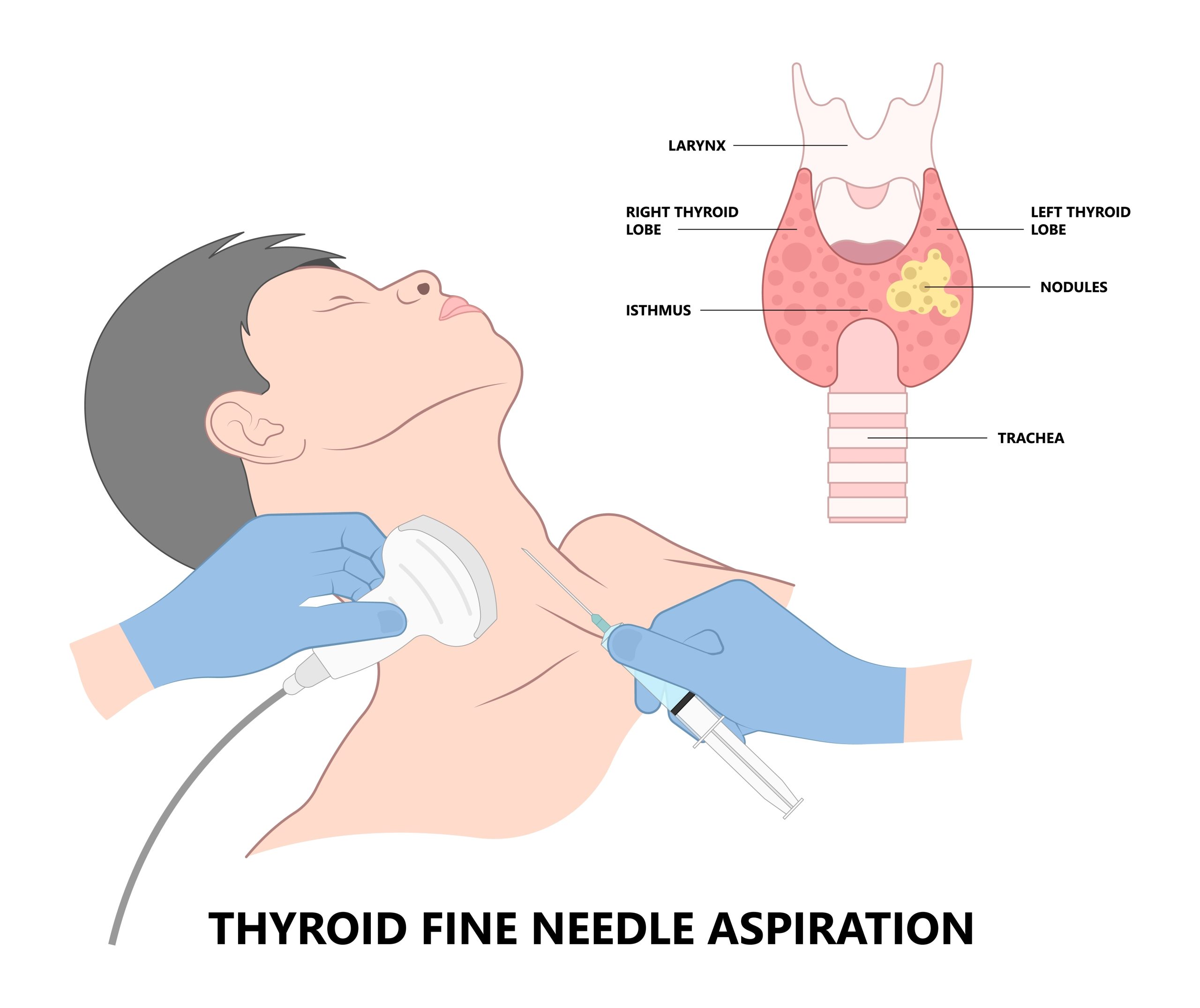
- Liver Biopsy: A needle is injected into the liver through the skin on the belly, capturing liver tissue.
- Kidney Biopsy: Similar to a liver biopsy, a needle is injected through the skin on the back, into the kidney.
- Aspiration Biopsy: A needle withdraws material out of a mass. This simple procedure is also called fine-needle aspiration.
DRAINAGE
DRAINAGE
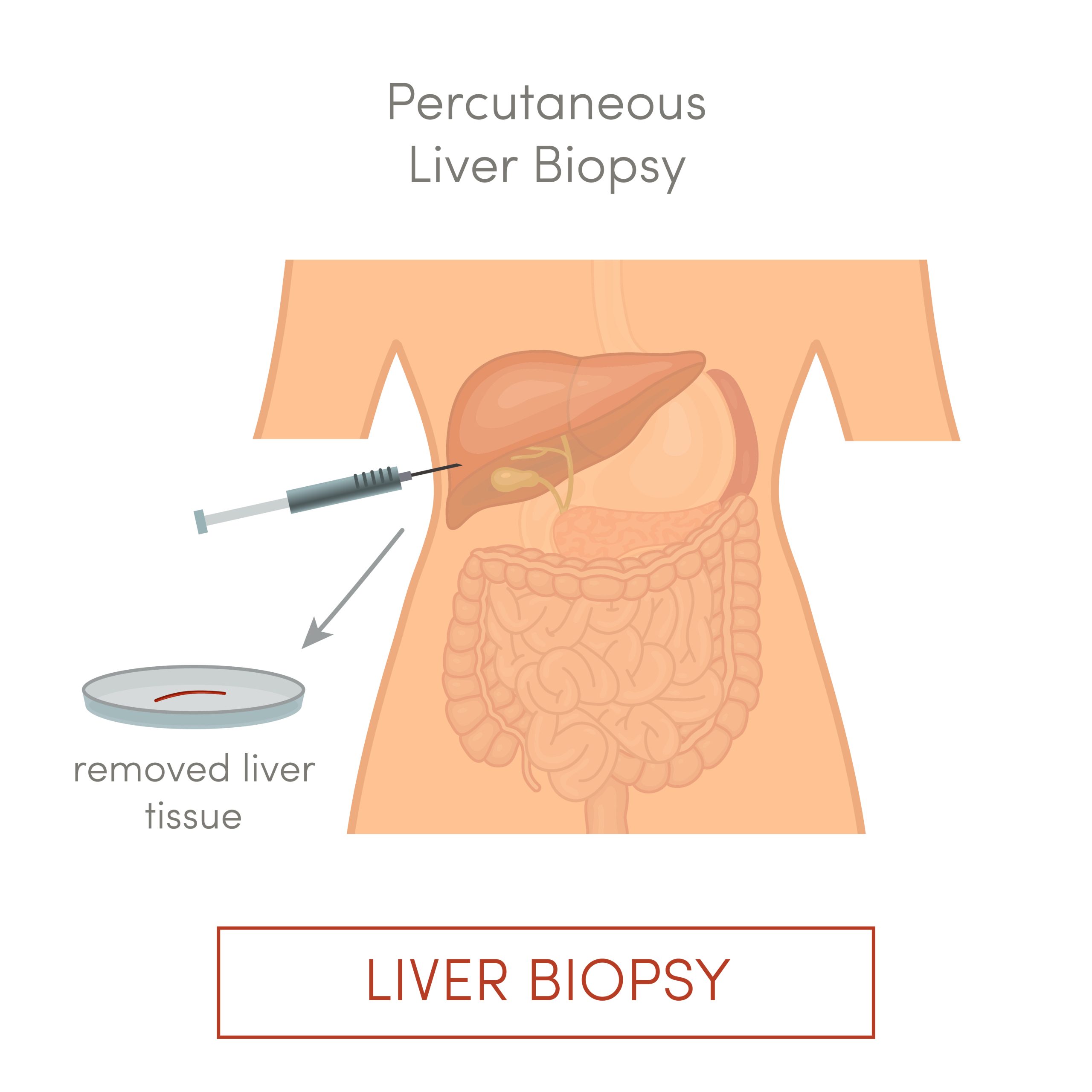
A fluid aspiration and drainage is a medical procedure in which a needle is passed through the skin, using image guidance (CT scan/X-ray/Ultrasound), into an abnormal fluid collection in order to remove the fluid. Some patients have all their fluid drained at one time or just a sample taken. Other patients are discharged with a drainage catheter in place.